Vympel R-77 on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The Vympel NPO R-77 missile (
 The aerodynamics are novel, combining vestigial cruciform wings with
The aerodynamics are novel, combining vestigial cruciform wings with
 * R-77 (''izdeliye'' 170) – Standard model.
* RVV-AE (''izdeliye'' 190) – Export model of the R-77. The missile has a maximum range of with 22.5 kg warhead.
* R-77-1 (''izdeliye'' 170-1) – Russian-built variant with a streamlined nose, 9B-1248 (''Izdeliye-50-1'') active radar seeker head, and new fins.
* RVV-SD – Export model of the R-77-1. The missile has a maximum range of with 22.5 kg warhead.
* R-77P / RVV-PE – Passive homing model.
* R-77T / RVV-TE – Infrared homing model.
* R-77-SRK – Ship-to-air variant.
* R-77-ZRK / RVV-AE-ZRK – RVV-ZRK Surface-to-air variant.
* R-77-PD / RVV-AE-PD – Ramjet model.
* R-77-PD ZRK / RVV-AE-ZRK – RVV-(PD-)ZRK Surface-to-air variant.
* K-77M (''izdeliye'' 180) – Version under development for the Sukhoi Su-57 with
* R-77 (''izdeliye'' 170) – Standard model.
* RVV-AE (''izdeliye'' 190) – Export model of the R-77. The missile has a maximum range of with 22.5 kg warhead.
* R-77-1 (''izdeliye'' 170-1) – Russian-built variant with a streamlined nose, 9B-1248 (''Izdeliye-50-1'') active radar seeker head, and new fins.
* RVV-SD – Export model of the R-77-1. The missile has a maximum range of with 22.5 kg warhead.
* R-77P / RVV-PE – Passive homing model.
* R-77T / RVV-TE – Infrared homing model.
* R-77-SRK – Ship-to-air variant.
* R-77-ZRK / RVV-AE-ZRK – RVV-ZRK Surface-to-air variant.
* R-77-PD / RVV-AE-PD – Ramjet model.
* R-77-PD ZRK / RVV-AE-ZRK – RVV-(PD-)ZRK Surface-to-air variant.
* K-77M (''izdeliye'' 180) – Version under development for the Sukhoi Su-57 with
NATO reporting name
NATO reporting names are code names for military equipment from Russia, China, and historically, the Eastern Bloc (Soviet Union and other nations of the Warsaw Pact). They provide unambiguous and easily understood English words in a uniform manne ...
: AA-12 Adder) is a Russian active radar homing
Active radar homing (ARH) is a missile guidance method in which a missile contains a radar transceiver (in contrast to semi-active radar homing, which uses only a receiver) and the electronics necessary for it to find and track its target aut ...
beyond-visual-range air-to-air missile
The newest and the oldest member of Rafael's Python family of AAM for comparisons, Python-5 (displayed lower-front) and Shafrir-1 (upper-back)
An air-to-air missile (AAM) is a missile fired from an aircraft for the purpose of destroying a ...
. It is also known by its export designation RVV-AE. It is the Russian counterpart to the American AIM-120 AMRAAM
The AIM-120 Advanced Medium-Range Air-to-Air Missile, or AMRAAM (pronounced ), is an American beyond-visual-range air-to-air missile (BVRAAM) capable of all-weather day-and-night operations. It is 7 inches (18 cm) in diameter, and employs ...
missile.
The R-77 was marked by a severely protracted development. Work began in the 1980s, but was not completed before the Soviet Union fell. For many years, only the RVV-AE model was produced for export customers. Production was further disrupted when the Russian invasion of Ukraine resulted in a Ukrainian arms embargo
An arms embargo is a restriction or a set of sanctions that applies either solely to weaponry or also to "dual-use technology." An arms embargo may serve one or more purposes:
* to signal disapproval of the behavior of a certain actor
* to maintain ...
against Russia, severing supply chain
In commerce, a supply chain is a network of facilities that procure raw materials, transform them into intermediate goods and then final products to customers through a distribution system. It refers to the network of organizations, people, acti ...
s. The Russian Air Force
" Air March"
, mascot =
, anniversaries = 12 August
, equipment =
, equipment_label =
, battles =
, decorations =
, bat ...
finally entered the R-77-1 (AA-12B) into service in 2015. It was subsequently deployed by Su-35S
The Sukhoi Su-35 (russian: link=no, Сухой Су-35; NATO reporting name: Flanker-E) is the designation for two improved derivatives of the Su-27 air-defence fighter. They are single-seat, twin-engine, supermaneuverable aircraft, design ...
fighters in Syria on combat air patrols. The export model of the R-77-1 is called RVV-SD.
Development
Work on the R-77 began in 1982. It represented Russia's first multi-purpose missile for tactical and strategic aircraft for fire-and-forget use against aircraft ranging from hovering helicopters to high-speed, low-altitude aircraft. Gennadiy Sokolovski, general designer of the Vympel Design Bureau, said that the R-77 missile can be used against medium and long range air-to-air missiles such as theAIM-120 AMRAAM
The AIM-120 Advanced Medium-Range Air-to-Air Missile, or AMRAAM (pronounced ), is an American beyond-visual-range air-to-air missile (BVRAAM) capable of all-weather day-and-night operations. It is 7 inches (18 cm) in diameter, and employs ...
and AIM-54 Phoenix, as well as SAMs such as the Patriot. The munition has a laser-triggered proximity fuze
A proximity fuze (or fuse) is a Fuze (munitions), fuze that detonates an Explosive material, explosive device automatically when the distance to the target becomes smaller than a predetermined value. Proximity fuzes are designed for targets such ...
and an expanding rod warhead that can destroy targets of various sizes. It can be used against cruise missiles and precision-guided munition
A precision-guided munition (PGM, smart weapon, smart munition, smart bomb) is a guided munition intended to precisely hit a specific target, to minimize collateral damage and increase lethality against intended targets. During the First Gul ...
s (PGMs). First seen in 1992 at the Moscow Airshow (MAKS) 1992, the R-77 was immediately nicknamed Amraamski by Western journalists. The basic R-77 is known as the ''izdeliye'' 170, while the export variant is known as the ''izdeliye'' 190 or RVV-AE. The R-77 and RVV-AE have a range of .Butowski, Piotr. ''Russia and CIS Observer''. 17 June 2007. Vympel did not have adequate funding during the 1990s and the first part of the following decade to support further evolution of the R-77, either for the Russian air force or the export market. The basic version of the R-77 is not thought to have entered the Russian air force inventory in significant numbers.
The R-77 can be used by upgraded Su-27, MiG-29 and MiG-31 variants in Russian Air Force service. Some variants of the Su-27 in China's People's Liberation Army Air Force, including the domestically produced J-11 variants, can also employ the missile. The newer Su-30MKK has a N001 (Su-27 radar) with a digital bypass channel incorporating a mode allowing it to use R-77s. The export RVV-AE has been sold widely, with China and India placing significant orders for the munition, as was the case for the R-73. The baseline R-77 was designed in the 1980s, with development complete by around 1994. India was the first export customer for the export variant, known as the RVV-AE, with the final batch delivered in 2002.
There are other variants under development. One has an upgraded motor to extend a range at high altitudes to as much as 120–160 km; it is known as the RVV-AE-PD (''Povyshenoy Dalnosti''—improved range). This variant has been test-fired and uses a solid-fuel ramjet engine. Its range puts it in the long-range class and is equivalent in range to the AIM-54 Phoenix. In another version of the R-77, a terminal infrared homing
Infrared homing is a passive weapon guidance system which uses the infrared (IR) light emission from a target to track and follow it seamlessly. Missiles which use infrared seeking are often referred to as "heat-seekers" since infrared is radi ...
seeker is offered. This is in line with the Russian practice of attacking targets by firing pairs of missiles with different homing systems. This complicates end-game defensive actions for the target aircraft, as it needs to successfully defeat two homing systems. If a radar-guided medium-range missile is fired at an enemy jet aircraft outside the non-escape attack zone, the target aircraft may be able to escape through emergency maneuver. But at this moment, in fact, the infrared guidance has an advantage: once the jet aircraft turns to escape, the engine nozzle is exposed, and the infrared characteristics are exposed. This method of attack may not always be available as IR seekers typically have less range and less resistance to poor weather than radar seekers, which may limit the successful use of mixed seeker attacks unless the IR missile is initially directed by radar or some other means.
Another improvement program was designated the R-77M, which made the missile longer and heavier, making use of a two-stage motor as well as an improved seeker. A further product-improvement of the R-77, designated the R-77M1 and then the R-77-PD, was to feature a ramjet propulsion device. This missile was destined for the MiG 1.44
The Mikoyan Project 1.44/1.42 (russian: link=no, Микоян МиГ-1.44; NATO reporting name: Flatpack) was a multirole combat aircraft, multirole fighter technology demonstrator developed by the Mikoyan design bureau. It was designed for the ...
that for the MFI program. The munition has a laser fuse and an expanding rod warhead that can destroy the variable sized targets. However, due to funding shortage and eventual cancellation of the MiG 1.44, development of this model may have stopped by 1999; no information or announcement regarding the R-77M and R-77-PD has appeared since.
Further development
Tactical Missile Weapons Corporation, also known as TRV (''Takticheskoe Raketnoe Vooruzhenie – Тактическое Ракетное Вооружение''), unveiled the RVV-SD and RVV-MD missiles for the first time at the Moscow Air Show (MAKS) in August 2009. The RVV-SD is an improved version of the R-77, while the RVV-MD is a variant of the R-73. The RVV-SD includes the upgrades associated with the ''izdeliye'' 170-1, or R-77-1. The RVV-SD, along with the RVV-MD, seem to be part of Russia's bid for India's medium multirole combat aircraft competition. Both designations were included by MiG on a presentation covering MiG-35 Fulcrum armament during Aero India Air Show in February. The initial RVV-SD offering is likely no more than a stopgap to try to maintain its position, and to provide a credible radar-guided weapon to offer as part of fighter export packages and upgrade programs.Barrie, Douglas and Pyadushkin, Maxim. "R-77, R-73 Missile Upgrades Emerge". '' Aviation Week''. 13 August 2009 According to specifications, the R-77-1 and its export variant RVV-SD is heavier than the basic R-77 / RVV-AE, weighing rather than . Maximum range is increased to from . The missile is also slightly longer at , rather than the of the basic variant. Additional improvements include upgrades to the missile's radar seeker and boat tail rear section to reduce drag. Russian missile manufacturer Agat previously confirmed it was working on seeker upgrades for the R-77, implying that at least two projects were underway, one for export and one for the Russian air force. Vympel, a which had merged to be part of TRV, has been developing a more extensive upgrade of the missile than the R-77-1. Designated the ''izdeliye'' 180, or K-77M, this missile is a mid-life upgrade for the missile and is intended to be the main medium-range missile for the Sukhoi Su-57. This upgrade aims to provide a further improvement in range, with the design including a dual-pulse motor configuration. The ''izdeliye'' 180 will use anActive electronically scanned array
An active electronically scanned array (AESA) is a type of phased array antenna, which is a computer-controlled array antenna in which the beam of radio waves can be electronically steered to point in different directions without moving the an ...
seeker and conventional rear fins instead of the R-77's lattice fins. This missile is intended to match the performance of the latest AIM-120 variants. Though it uses a similar designation as the earlier R-77M improvement program, it is not known if these two missiles are the same or are related.
On October 4, 2020 footage of Su-57 fighter flying with R-77M missile was revealed in a video released by the Russian Defense Ministry commemorating the 100th anniversary of the 929th Chkalov State Flight-Test Center
Design description
 The aerodynamics are novel, combining vestigial cruciform wings with
The aerodynamics are novel, combining vestigial cruciform wings with grid fin
Grid fins (or lattice fins) are a type of flight control surface used on rockets and bombs, sometimes in place of more conventional control surfaces, such as planar fins. They were developed in the 1950s by a team led by and used since the 197 ...
s used as tail control surfaces (similar devices are used on the OTR-23 Oka, and USAF uses them on MOAB
Moab ''Mōáb''; Assyrian: 𒈬𒀪𒁀𒀀𒀀 ''Mu'abâ'', 𒈠𒀪𒁀𒀀𒀀
''Ma'bâ'', 𒈠𒀪𒀊 ''Ma'ab''; Egyptian: 𓈗𓇋𓃀𓅱𓈉 ''Mū'ībū'', name=, group= () is the name of an ancient Levantine kingdom whose territo ...
). The flow separation which occurs at high angles of attack enhances its turning ability, giving the missile a maximum turn rate of up to 150° per second. However, the grid fins also increase drag and radar cross section. Updated variants of the R-77, such as the ''izdeliye'' 180 that is destined for the Sukhoi Su-57, will use conventional fins instead.
The missile uses a multi-function doppler- monopulse active radar seeker developed by OAO Agat. The radar features two modes of operation, over short distances, the missile will launch in an active " fire-and-forget" mode. Over longer distances the missile is controlled by an inertial guidance auto pilot with occasional encoded data link updates from the launch aircraft's radar on changes in spatial position or G of the target. As the missile comes within of its target, the missile switches to its active radar mode. The host radar system maintains computed target information in case the target breaks the missile's lock-on.
Operational history
At the beginning of February 2016, four Su-35S were deployed to Syria as part of the Russian aerial expeditionary force to the country. Tasked with air to air duties, the Su-35S were extensively documented while armed with a couple of R-77 missiles, between IR seeking R-27T under the inner pylons and R-73 under the outer ones.Variants
AESA
Aesa or Aisa ( grc, Αἶσα) was a town of ancient Macedonia. Aesa belonged to the Delian League since it appears on a tribute list to Athens in 434/3 BCE. The editors of the Barrington Atlas of the Greek and Roman World identify Aesa wi ...
seeker, conventional fins, and two-pulse motor.
* K-77ME (''izdeliye'' 180-BD) – Ramjet model of the K-77M.
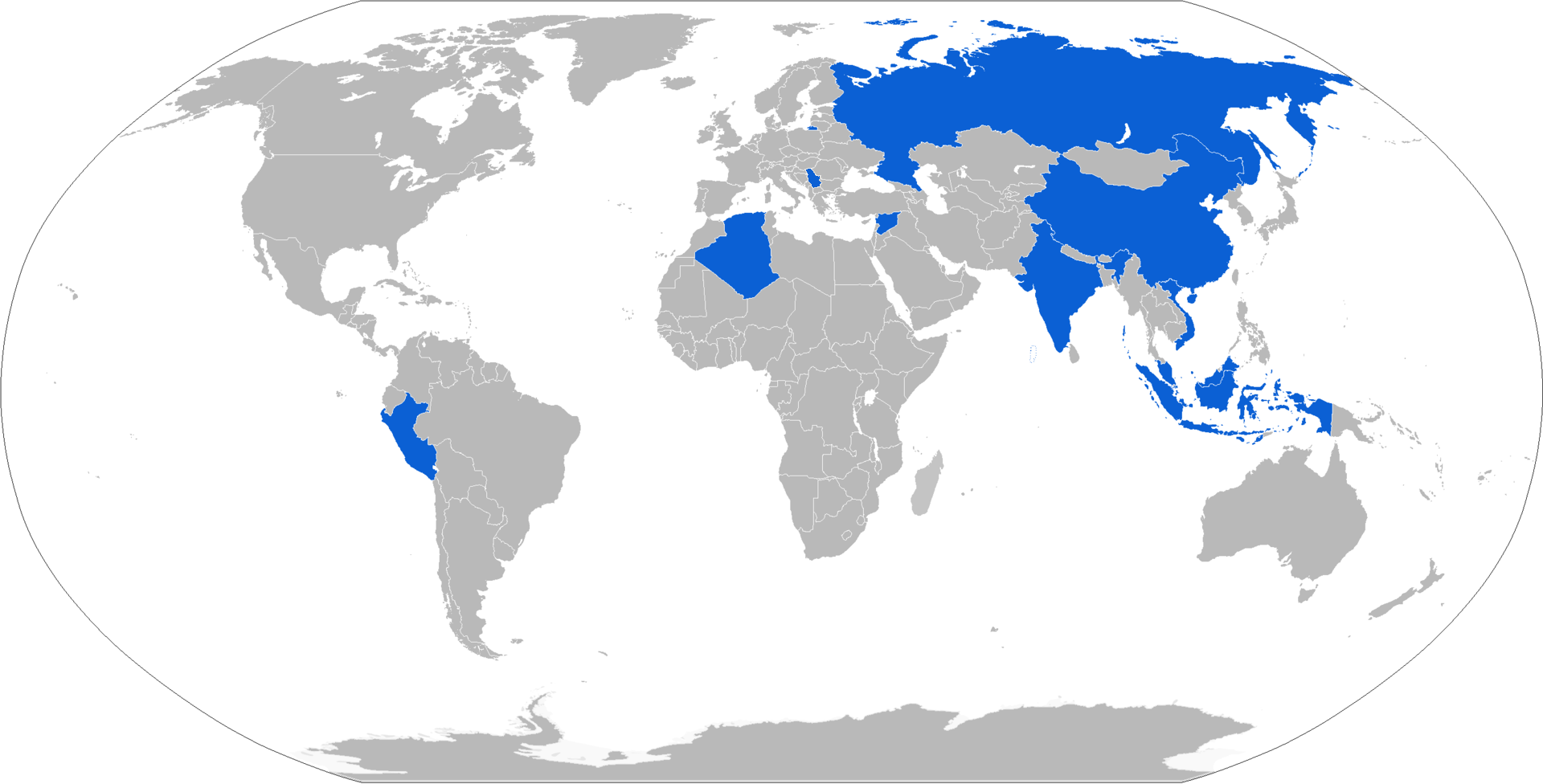
Operators

Current operators
* – for the MIG-29M/M2 and Su-30MKA * – unknown number bought in 2013 * – 300 for the MIG-29M/M2 and Su-35 * – for the Su-30MKK and Su-30MK2 ** People's Liberation Army Air Force ** People's Liberation Army Naval Air Force * – for the MiG-21UPG, MiG-29UPG and Su-30MKI. Received 500 missiles in 2014-15, ordered 400 more in 2019 ** Indian Naval Air Arm * – for the Su-30MK2 and Su-27SKM * – for the Su-30SM * – 150 missiles delivered for use on Sukhoi Su-30MKMs * – basic variant never officially introduced in series, Su-30SMs and Su-35S' were spotted with R-77-1s when they were deployed to Syria. 2 contracts have reportedly been signed in 2015 for 13 billion rubles and in 2020 concerning modernized and import-substituted missiles for 65 billion rubles. * – Serbia ordered 200 R-77-1 missiles for modernized MiG-29s * – for the MiG-29SE * – for the MiG-29SM * * – 100 missiles ordered for Su-30MK2s * – for the Su-30MK2 * – 100 missiles delivered by 2005 for MiG-29SMsFormer operators
* – used for a short time on MiG-29sSee also
* List of missiles *AAM-4
The Mitsubishi AAM-4 (Type 99 air-to-air missile, ) is a medium-range active radar homing air-to-air missile. It is a modern beyond-visual-range missile developed in Japan and intended to replace the semi-active radar homing AIM-7 Sparrow missile ...
* Astra Mark 1
* Python (missile)
* Meteor (missile)
* PL-12
* PL-15
* PL-21
*AIM-120 AMRAAM
The AIM-120 Advanced Medium-Range Air-to-Air Missile, or AMRAAM (pronounced ), is an American beyond-visual-range air-to-air missile (BVRAAM) capable of all-weather day-and-night operations. It is 7 inches (18 cm) in diameter, and employs ...
* Long-Range Engagement Weapon
References
;Citations ;Bibliography * {{DEFAULTSORT:R077 (Missile) Air-to-air missiles of Russia Air-to-air missiles of the Soviet Union Cold War air-to-air missiles of the Soviet Union Vympel NPO products Military equipment introduced in the 2000s Fire-and-forget weapons